The United Kingdom’s Gambling Commission has released a report finding that 11% of 11-16 year olds surveyed had participated in some form of gambling. The survey was performed using Ipsos MORI’s Young People Omnibus, which is a survey of various schools primarily in England and Wales, with a few schools in Scotland in the sample. The overall rates of gambling have dropped 4% since 2016, and continued a downward trend since 2011, where 23% of students surveyed had reported gambling.
The report looked at all types of gambling, notably online games made to resemble traditional gambling, in-game/app gambling, slot machines (referred to in British English and the report as “Fruit Machines”), card games, and the UK’s national lottery. The report notes that the most common way of online gambling is using an app on a phone or tablet, followed by games on sites such as Facebook, free demos, and other websites.
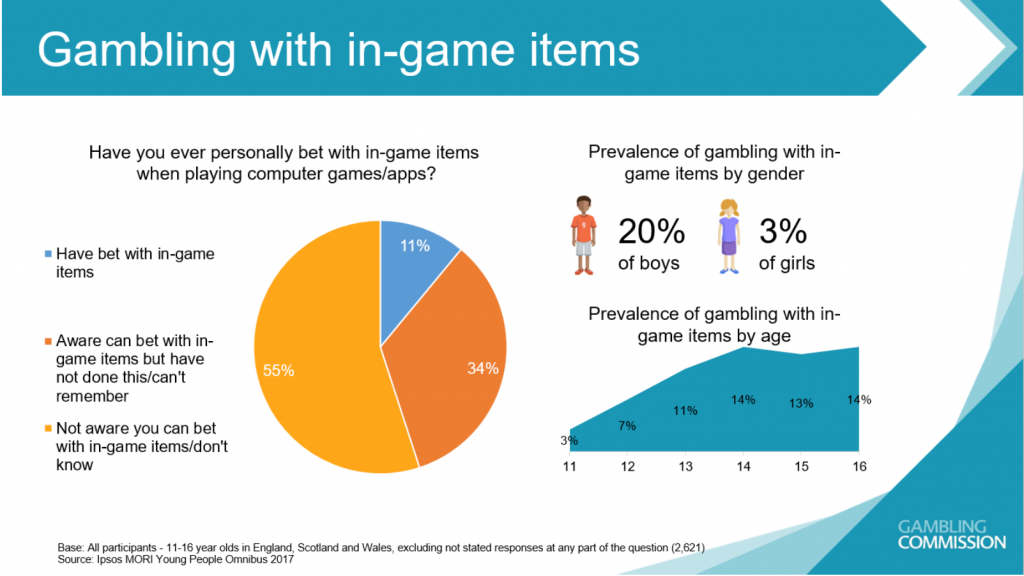
Of particular note is the new section focusing specifically on cosmetic items within video games. The report takes the position that because there are ways to convert these items to cash or to trade them, they have real world value, in particular with regards to Skins that are used for betting, such as those in Counter-Strike: Global Offensive (also seen in the newly released PUBG). Of those students that played these games, 11% said that they have gambled with in-game items, while another 55% said that they knew of gambling but had not done so. A further 34% was unaware of this possibility.
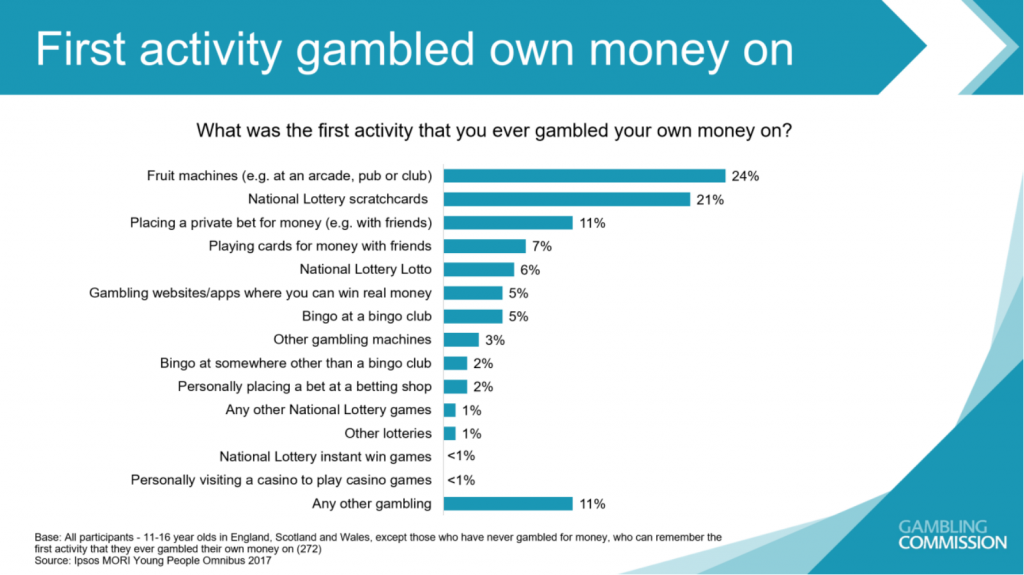
The most common age at which a student first gambled is 12, and most often for the reason of excitement (41%). The other most common reasons were to make money (40%) and for entertainment (33%). Curiosity was given as a reason in 26% of students, and boredom another 20%. The most common methods were slot machines, lottery, and private games with friends.
The report concludes that 0.9% of 11-6 year olds are problem gamblers as defined by DSM-IV criteria. Under this criteria, preoccupation, tolerance, withdrawal, loss of control, escape, chasing, lying, illegal acts, and risked relationships are checked.
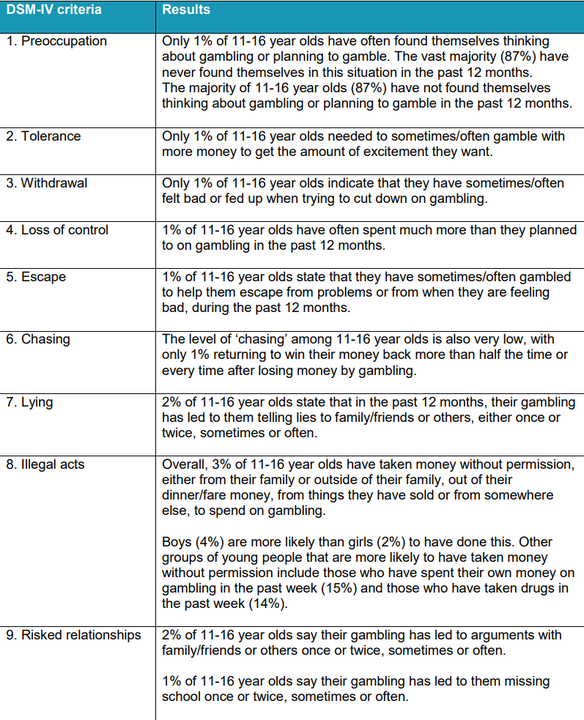
A child expressing four or more of the behaviors is considered a problem gambler. Two or three is considered an at-risk gambler, and zero to one is considered a non-problem gambler. The rates of problem gamblers has increased 0.5% since 2016, but the report also cautions that it is not directly comparable because of a change in sample definition.
What do you think of online gambling? Have you had any issues or known anybody that has had issues with it? Let us know in the comments.







